Anxiety, an unwelcome companion, grips the mind in a relentless embrace. Its tendrils weave through thoughts, whispering doubt and fear. Heartbeats quicken, breaths shallow, as the weight of imagined calamities presses down. Rationality falters in the face of irrational worries, creating a suffocating fog that obscures reality. The incessant what-ifs echo, amplifying the sense of impending doom. Yet, anxiety is a universal human experience, a reminder of vulnerability. Acknowledging its presence is the first step towards reclaiming control. In the quiet struggle, courage emerges, unraveling the anxious threads that entwine the soul, paving the way for peace and resilience.
DIFFERENT TYPE OF ANXIETY
Agoraphobia is an anxiety disorder characterized by an intense fear of situations or places where escape might be difficult, leading to avoidance of public spaces. Individuals with agoraphobia may dread open spaces, crowded areas, or situations where they feel trapped and unable to seek help. This fear often results in social isolation as those affected strive to minimize distressing encounters. Cognitive-behavioral therapy and exposure techniques are commonly employed to help individuals gradually confront and overcome their fears, reclaiming a sense of freedom in navigating the world.

Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) is a chronic mental health condition marked by excessive and uncontrollable worry about various aspects of life, even in the absence of specific triggers. Individuals with GAD often experience persistent anxiety, restlessness, and physical symptoms like muscle tension or fatigue. The pervasive nature of their concerns can impact daily functioning. Treatment typically involves therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and sometimes medication to alleviate symptoms and improve coping mechanisms, fostering a better quality of life.
Panic disorder is a debilitating anxiety condition characterized by recurrent and unexpected panic attacks. These episodes involve intense fear, palpitations, shortness of breath, and a sense of impending doom. Sufferers often live in constant fear of future attacks, leading to avoidance behavior. Therapy, including cognitive-behavioral techniques and medications, is commonly employed to manage symptoms and empower individuals to regain control over their lives.
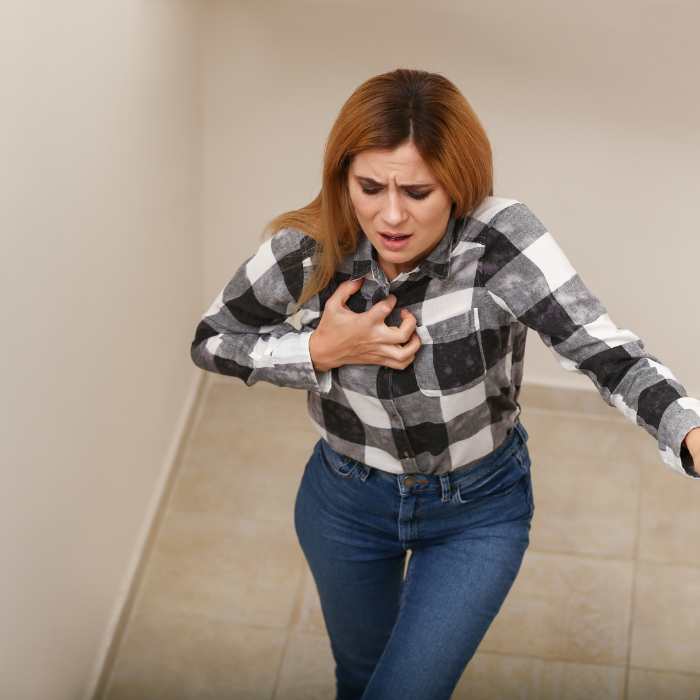


Phobias are irrational and intense fears of specific objects, situations, or activities, triggering excessive anxiety and avoidance behaviors. Common phobias include heights, spiders, or flying. These fears can disrupt daily life and relationships. Cognitive-behavioral therapy, exposure therapy, and medications are often used to help individuals confront and manage phobias, enabling them to lead more fulfilling and unrestricted lives.
Separation Anxiety Disorder is a psychological condition characterized by excessive fear or anxiety about being separated from individuals to whom a person is emotionally attached. Common in childhood, it may persist into adulthood, impacting daily functioning. Symptoms include distress, nightmares, and physical complaints when anticipating or experiencing separation. Therapy, particularly cognitive-behavioral approaches, helps individuals develop coping strategies to alleviate separation-related distress.
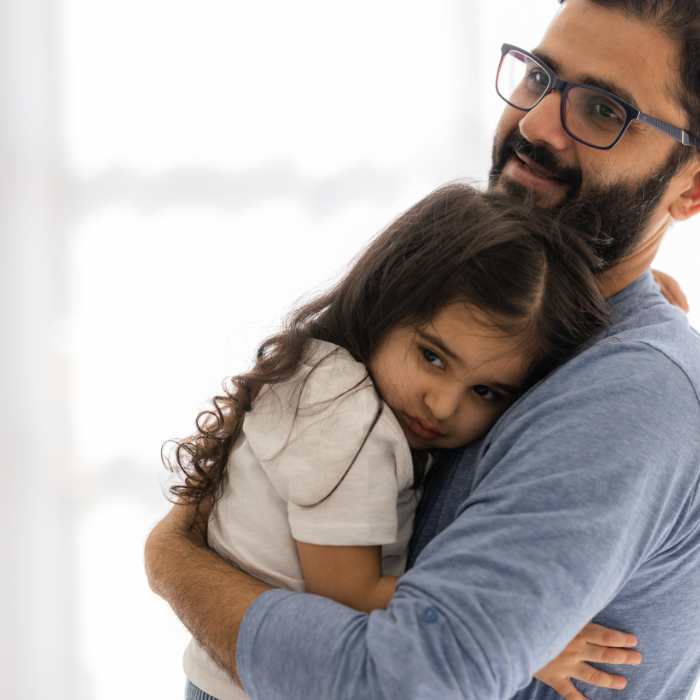


Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD) is an intense fear of social situations, where individuals worry about negative judgment and embarrassment. It can hinder daily interactions, leading to avoidance of social gatherings or performance situations. Physical symptoms like blushing or trembling may accompany the anxiety. Therapy, including cognitive-behavioral techniques, exposure therapy, and medication, helps manage symptoms and fosters increased confidence in social settings, facilitating improved social relationships and overall well-being.
Practice mindfulness, deep breathing, and seek support from loved ones. Professional therapy or counseling can provide effective coping strategies.

